Introduction to Electronics

What You’ll Learn
- Basic components of electronics
- Basic operation in electronic circuits
- Some common applications of eletronics
Electronics can be defined as a branch of physics that deals with the study of electron behavior, flow, and control under different conditions. Such conditions include vacuums, gases, or semiconducting materials where electrons are observed. Electronics is the study of how to control the flow of electrons. It deals with circuits made up of components that control the flow of electricity. The identification of the electron in 1897, along with the subsequent invention of the vacuum tube which could amplify and rectify small electrical signals, inaugurated the field of electronics and the electron age. Vacuum tubes (Thermionic valves) were among the earliest electronic components. This distinction started around 1906 with the invention by Lee De Forest of the triode, which made electrical amplification of weak radio signals and audio signals possible with a non-mechanical device.
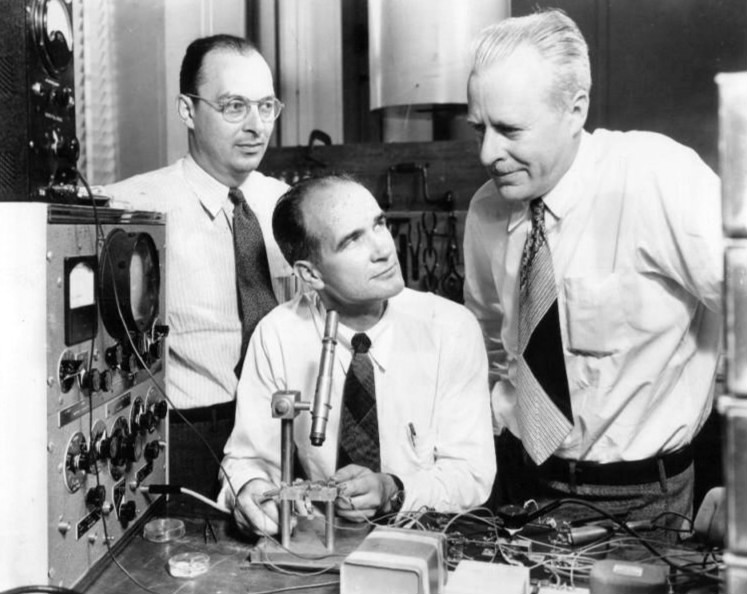
The first working transistor was invented by William Shockley, Walter Houser Brattain, and John Bardeen at Bell Labs in 1947. The MOSFET (MOS transistor) was later invented by Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in 1959. The first working point-contact transistor was invented by John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brattain at Bell Labs in 1947.

- 4 Sections
- 0 Lessons
- 10 Weeks
- Introduction to Electronics0
- Power amplifiers0
- Operational amplifiers0
- Circuit Theory0
wikimaster
Access quality education without the cost. Explore top courses and programs in Free. Affordable education ensures that every individual, regardless of their economic background, has access to opportunities for intellectual growth.
Get unlimited access to all learning content and premium assets Membership Pro
You might be interested in
-
All levels
-
0 Students
-
0 Lessons
-
All levels
-
0 Students
-
0 Lessons
-
All levels
-
0 Students
-
0 Lessons
-
All levels
-
0 Students
-
0 Lessons
Sign up to receive our latest updates
Get in touch
Call us directly?
Address